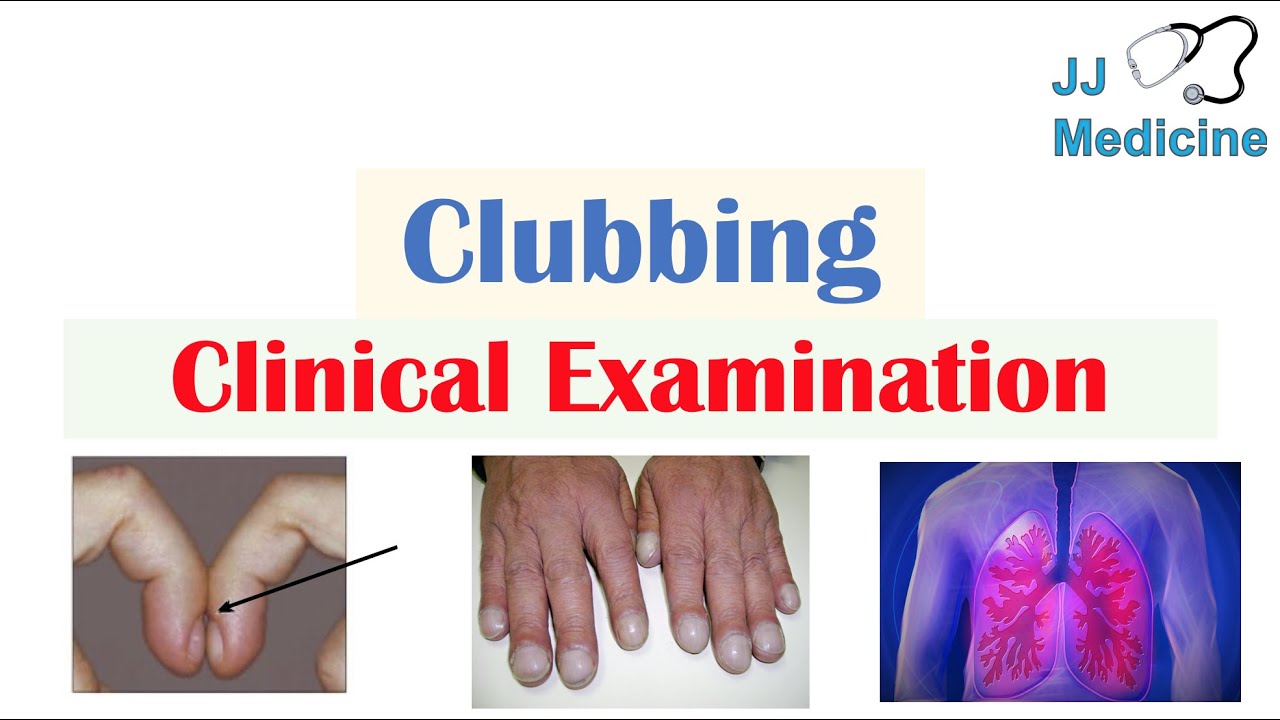
Understanding the Manifestations and Management of This Condition
This condition, characterized by specific symptoms, necessitates appropriate treatment strategies. Identifying these symptoms and understanding effective treatment protocols are crucial for prompt and successful intervention. Proper management can lead to improved quality of life and potentially prevent long-term complications.
The symptoms often include pain, swelling, and limited mobility in affected areas. Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, imaging studies (such as X-rays or MRIs), and potentially a biopsy. Treatment approaches vary depending on the severity and underlying cause, and may include medications, physical therapy, or, in severe cases, surgical intervention. Monitoring of the condition is essential for optimal outcomes.
While the exact prevalence and specific risk factors associated with this condition remain under research, appropriate management of the identified symptoms is essential for improved health outcomes. Early diagnosis and timely interventions can mitigate long-term implications. This understanding allows healthcare professionals to provide effective care, leading to improved patient well-being.
Let's delve into the specifics of identifying symptoms, effective treatment options, and the overall management of this condition.
Clubitis Disease Symptoms and Treatment
Understanding the symptoms and effective treatments for clubitis is vital for timely intervention and improved patient outcomes. Accurate identification and appropriate management are essential.
- Pain
- Swelling
- Limited Mobility
- Inflammation
- Diagnosis
- Physical Therapy
- Medications
- Surgical Intervention
These key aspects highlight the multifaceted nature of clubitis. Pain and swelling are common initial symptoms. Limited mobility underscores the functional impact, demanding careful consideration of physical therapy. Proper diagnosis is crucial for tailoring treatment. Medications and, in severe cases, surgical intervention are potential aspects of treatment. A holistic approach involving pain management, mobility restoration, and tailored intervention are crucial for optimal outcomes. For instance, a diagnosis of clubitis might involve X-rays to assess bone development, alongside therapies to address inflammation and restore functionality.
1. Pain
Pain is a prominent feature in clubitis, often serving as a primary indicator of the condition's presence. Understanding the nature of this pain, its location, and its intensity aids in diagnosis and treatment planning. The experience of pain varies, reflecting the underlying pathology and individual responses. Accurate characterization is critical for appropriate medical intervention.
- Location and Characterization of Pain
Pain in clubitis is often localized to the affected joint or surrounding tissues. Its character can vary, from a dull ache to sharp, throbbing sensations. The precise location and nature of pain can offer clues regarding the specific structures involved and the severity of the condition. Precise descriptions, such as "deep," "aching," or "burning" pain, assist clinicians in differentiating clubitis from other conditions.
- Severity and Duration of Pain
Pain severity can range from mild discomfort to intense agony. The duration of pain is also a diagnostic factor, helping distinguish between acute and chronic conditions. The persistence or fluctuation of pain over time is a component in the assessment. This information influences treatment approaches and prognosis.
- Pain and Functional Impact
The intensity and duration of pain directly influence the affected individual's ability to perform daily activities. Pain significantly limits mobility and function, impacting overall quality of life. The relationship between pain and the degree of disability guides treatment decisions and emphasizes the importance of pain management strategies in the overall treatment plan for clubitis.
- Pain as a Symptom of Underlying Pathology
Pain experienced in clubitis serves as a symptom, reflecting underlying structural or inflammatory changes. The presence of pain, its location, and its characteristics contribute to understanding the underlying etiology of the condition. This knowledge directs treatment strategies toward addressing the root cause of the pain, leading to a more effective and comprehensive approach to managing clubitis.
In summary, pain plays a multifaceted role in the presentation, diagnosis, and management of clubitis. Careful consideration of pain location, character, severity, duration, and functional impact is crucial. This detailed understanding of pain empowers healthcare professionals to implement targeted treatments and optimize patient outcomes.
2. Swelling
Swelling, a common symptom in clubitis, arises from various inflammatory processes. The presence and characteristics of swelling provide valuable diagnostic information. Understanding the relationship between swelling and clubitis is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Swelling, frequently accompanied by pain and limited mobility, indicates underlying inflammation and tissue damage. Inflammation, a natural response to injury or infection, triggers fluid accumulation, manifesting as swelling in the affected area.
The degree and location of swelling offer clues about the severity and potential site of the inflammatory process. Significant swelling, for example, in a joint associated with pain and restricted movement, strongly suggests involvement of that joint in the inflammatory response characteristic of clubitis. Proper assessment of swelling size, consistency, and location informs the selection of appropriate diagnostic procedures and guides treatment decisions. Identifying the underlying cause of swelling, whether related to trauma, infection, or another contributing factor, is critical for tailoring treatment strategies and potentially preventing future complications. Monitoring changes in swelling over time, in conjunction with other clinical findings, aids in assessing treatment efficacy and the overall response to intervention.
In conclusion, swelling in clubitis is a key symptom reflecting the inflammatory cascade. Careful evaluation of the location, extent, and characteristics of swelling are critical for proper diagnosis and management. By understanding the connection between swelling and the underlying pathophysiological processes, healthcare professionals can effectively tailor treatment strategies to address the root cause of the inflammation and promote optimal outcomes for patients.
3. Limited Mobility
Limited mobility is a significant symptom associated with clubitis. This restriction in movement directly impacts the individual's functional capacity and quality of life. Understanding the different aspects of limited mobility within the context of clubitis is crucial for both diagnosis and effective treatment strategies.
- Impact on Daily Activities
Reduced mobility hinders the performance of everyday tasks. Simple activities like walking, climbing stairs, or reaching for objects become challenging or impossible. This limitation can significantly affect an individual's independence and ability to participate in social and occupational activities. The severity of this impact varies depending on the extent of the mobility restriction caused by clubitis.
- Pain and Discomfort as a Contributing Factor
Pain frequently accompanies limited mobility in clubitis. The discomfort associated with the affected joint or surrounding tissues restricts movement and aggravates pain. The cycle of pain and limited mobility can create a self-perpetuating problem, making it challenging to perform even simple tasks. Understanding this interplay is crucial for therapeutic interventions.
- Diagnostic Implications
Evaluation of limited mobility is an integral part of the diagnostic process. Assessing the extent and pattern of restricted movement helps distinguish clubitis from other musculoskeletal conditions. Comparing the affected area's range of motion with the unaffected side provides valuable diagnostic information. Measurement tools and objective assessments aid in identifying the specific degree of functional limitation and monitoring treatment progress.
- Treatment Implications
Limited mobility significantly influences treatment strategies. Physical therapy plays a vital role in restoring movement and improving range of motion. Therapeutic exercises and assistive devices are often prescribed to improve function and manage pain. The overall treatment plan considers how to address the specific limitations imposed by clubitis to maximize functional recovery.
In summary, limited mobility in clubitis is more than just a symptom; it's a critical component affecting an individual's entire life. Addressing this symptom through proper diagnosis, pain management, and rehabilitation strategies is essential for optimal outcomes and functional recovery.
4. Inflammation
Inflammation is a central component in clubitis, directly influencing the spectrum of symptoms and dictating treatment approaches. This inflammatory response, while a natural biological process, can become problematic when prolonged or excessive. The precise nature of the inflammatory process in clubitis influences the severity and duration of symptoms, requiring careful consideration in treatment planning.
The interplay between inflammation and clubitis symptoms is evident in the observed pain, swelling, and limited mobility. These features are direct consequences of the inflammatory cascade. Elevated levels of inflammatory mediators, such as cytokines and prostaglandins, contribute to the localized swelling and tenderness characteristic of the condition. Furthermore, the persistent inflammation can lead to structural damage, potentially affecting the long-term function of affected tissues and joints. Understanding this inflammatory component is crucial for devising effective treatment strategies that target both the immediate symptoms and the underlying mechanisms driving the inflammatory response. For example, anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce the intensity and duration of the inflammatory process, mitigating associated symptoms. In addition, non-pharmacological interventions, such as physical therapy and targeted exercise, can complement the reduction of inflammation, aiding in functional recovery. Without a comprehension of this inflammatory component, effective treatment protocols remain incomplete and less effective in achieving optimal outcomes.
In conclusion, inflammation serves as a pivotal element within the context of clubitis. Its presence directly correlates with the hallmark symptoms and substantially impacts the overall treatment approach. Effective management necessitates targeting the inflammatory process, not only to alleviate immediate symptoms but also to prevent long-term complications. Recognition of the intricate relationship between inflammation and clubitis is essential for creating targeted and comprehensive treatment plans, ultimately optimizing patient well-being and functional recovery.
5. Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis of clubitis is fundamental for effective treatment and positive patient outcomes. The diagnostic process relies heavily on the thorough evaluation of symptoms, physical examination findings, and supporting investigations. A precise diagnosis allows for tailored interventions, minimizing potential complications and optimizing the therapeutic approach.
- Symptom Evaluation
Careful consideration of reported symptoms is paramount. This encompasses not only the presence and intensity of pain, swelling, and limited mobility but also the location, duration, and any associated factors that might contribute to the condition. For example, recent trauma, infections, or underlying systemic diseases can influence the presentation of clubitis. A detailed patient history, including relevant medical background, aids in differentiating clubitis from other potential conditions.
- Physical Examination
A comprehensive physical examination plays a vital role. Assessment of affected joints involves evaluating range of motion, tenderness, warmth, and any visible signs of inflammation or deformity. Palpation and observation are essential to detect subtle signs, which might indicate the degree and location of the inflammatory response. Direct comparison with the unaffected side provides crucial context. Findings from the physical examination, combined with symptom evaluation, help formulate a preliminary hypothesis regarding the condition.
- Imaging Studies
Imaging modalities, such as X-rays and MRI scans, provide crucial anatomical details. X-rays can reveal bone abnormalities, while MRI scans provide insights into soft tissue structures, enabling a deeper understanding of the underlying pathology. These imaging techniques help determine the extent of damage and identify any potential complications. For instance, an MRI might reveal inflammation within the joint capsule or surrounding tissues, confirming suspicions raised by physical examination.
- Differential Diagnosis
Differentiating clubitis from other similar conditions is essential. Conditions exhibiting overlapping symptoms require careful analysis and may necessitate further investigations. This includes considering potential infections, other inflammatory arthritides, and trauma-related injuries. The process of differential diagnosis ensures that the most appropriate treatment pathway is followed.
In summary, the diagnostic approach to clubitis requires a multifaceted approach, combining symptom evaluation, physical examination, and appropriate imaging studies. This comprehensive evaluation allows clinicians to formulate an accurate diagnosis, enabling the implementation of a tailored treatment plan, thus facilitating positive patient outcomes.
6. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management of clubitis symptoms. The therapeutic approach focuses on restoring function and alleviating pain associated with the condition. Effective physical therapy programs are tailored to address individual needs and the specific characteristics of each case of clubitis. The rationale for incorporating physical therapy is rooted in its ability to address both the immediate symptoms and the underlying causes of the condition.
Specific interventions within a physical therapy program often include range-of-motion exercises to improve joint flexibility and reduce stiffness. Manual therapy techniques, such as soft tissue mobilization and joint manipulation, may be employed to alleviate pain and restore proper joint mechanics. Strengthening exercises, targeting the muscles surrounding the affected area, help to stabilize the joint and prevent further injury. Therapeutic modalities, such as heat or ice application, can be used to reduce pain and inflammation. Patient education regarding proper posture, body mechanics, and activity modification is also essential to prevent future exacerbations. For example, a patient with clubitis affecting the shoulder might undergo exercises focusing on improving shoulder flexion, abduction, and external rotation, alongside strengthening of the rotator cuff muscles. This personalized approach aims to maximize functional recovery and minimize long-term complications. Successful outcomes often depend on the adherence to the prescribed exercises and consistent engagement with the physical therapy program.
The integration of physical therapy into the overall management strategy for clubitis underscores its importance as a non-invasive and effective intervention. This approach promotes functional recovery, reduces dependence on pain medications, and empowers individuals to actively participate in their own rehabilitation. By targeting both the symptoms and the underlying mechanisms contributing to clubitis, physical therapy equips patients with the tools and knowledge to manage the condition effectively and improve their quality of life. However, the success of a physical therapy program for clubitis, as with any treatment, depends on consistent adherence to the prescribed plan, addressing any barriers to participation, and collaborating closely with healthcare professionals.
7. Medications
Medications play a significant role in managing clubitis symptoms and treating the underlying condition. Their application is dictated by the severity and specific characteristics of each case. The selection of appropriate medications hinges on the identification of the root causes contributing to clubitis. For instance, if inflammation is a primary driver, anti-inflammatory medications become crucial. Similarly, if pain is a dominant symptom, analgesic medications are integral to the treatment plan. The effectiveness of medications in alleviating symptoms depends on proper dosage, timing, and patient adherence to the prescribed regimen. A well-structured medication regimen can help control inflammation and pain, leading to improved mobility and overall quality of life.
Various types of medications are utilized in the management of clubitis. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed for their ability to reduce pain and inflammation. Corticosteroids, potent anti-inflammatory agents, are sometimes used to address severe inflammation. In cases where underlying autoimmune processes contribute to clubitis, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) might be considered to mitigate the long-term progression of the condition. Specific considerations are necessary when selecting medication, as some agents might have side effects or interactions with other medications. Careful monitoring of patients receiving these medications is paramount to assess efficacy, manage potential adverse effects, and ensure overall patient well-being. A combination of medications might be necessary to achieve optimal symptom control.
The critical role of medications in clubitis treatment is evident. Appropriate medication selection, tailored to the individual case, contributes significantly to symptom relief and long-term management. Understanding the diverse types of medications, their mechanisms of action, and potential side effects is essential for both healthcare providers and patients. This comprehensive understanding enables informed decisions regarding medication use, leading to more effective outcomes and improved quality of life for those affected by clubitis. However, it is vital to acknowledge that medications are not a standalone solution. They must be integrated within a comprehensive treatment plan encompassing lifestyle modifications, physical therapy, and patient education for optimal outcomes.
8. Surgical Intervention
Surgical intervention in clubitis disease management is considered a last resort, reserved for cases where conservative treatments prove ineffective or when the condition significantly compromises joint function. Its application depends heavily on the severity of the underlying pathology and the degree of functional impairment. The decision for surgical intervention is based on a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's specific situation, considering potential benefits and risks.
- Specific Indications for Surgery
Surgical intervention might be warranted for severe cases of clubitis that do not respond to non-surgical therapies or for conditions that cause significant joint damage. This could include cases of extensive cartilage damage or bone erosion. The presence of persistent and debilitating pain unresponsive to other treatments also becomes a strong indicator for surgical intervention. In some instances, deformities that restrict joint movement might necessitate surgical correction to restore functionality.
- Types of Surgical Procedures
The type of surgical procedure undertaken depends on the specific location and extent of the clubitis. Procedures might range from arthroscopic techniques for minimally invasive interventions to open surgeries in more complex cases. Reconstruction of damaged tissues, such as cartilage repair or bone grafts, can be integral components of these interventions. The goal is to address the underlying cause of the condition and restore normal joint function.
- Potential Complications and Risks
Surgical interventions carry inherent risks and potential complications, including infection, bleeding, nerve damage, and persistent pain. These risks need careful consideration when evaluating the appropriateness of surgery. The patient's overall health status and the specific nature of the condition influence the assessment of potential risks. Potential risks are part of a balanced evaluation of the advantages and drawbacks of surgery in a specific case.
- Post-Operative Rehabilitation
Successful surgical intervention for clubitis necessitates a diligent post-operative rehabilitation program. This often includes physical therapy to restore range of motion, strengthen surrounding muscles, and gradually increase activity levels. Compliance with the rehabilitation protocol is essential for achieving optimal outcomes and minimizing potential complications. Post-operative rehabilitation is tailored to the individual patient's needs and the specifics of the surgical procedure performed.
In conclusion, surgical intervention for clubitis represents a specialized approach for managing severe cases unresponsive to other treatments. Decisions regarding surgery are complex and must consider the specific condition, potential benefits, potential risks, and the patient's overall health status. Careful pre-operative evaluation and a comprehensive post-operative rehabilitation plan are crucial for successful outcomes. Surgery is a tool within the broader spectrum of treatments, strategically reserved for cases where other interventions prove insufficient.
Frequently Asked Questions about Clubitis
This section addresses common questions and concerns surrounding clubitis, its symptoms, and treatment options. Accurate information is essential for understanding the condition and making informed decisions regarding healthcare.
Question 1: What are the typical symptoms of clubitis?
Clubitis presents with a range of symptoms, often including pain, swelling, and limited mobility in the affected area. Pain may vary in character, from dull aches to sharp, throbbing sensations. Swelling may be localized to the joint or extend to surrounding tissues. Limited mobility directly impacts functional capacity, restricting the ability to perform daily activities. The specific symptoms and their severity can vary depending on the underlying cause and the individual's response to the condition.
Question 2: How is clubitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a comprehensive evaluation. Patient history, focusing on symptoms, their duration, and any potential contributing factors, is crucial. A physical examination assessing affected joints, range of motion, tenderness, and inflammation is performed. Imaging studies, such as X-rays or MRI scans, may be necessary to identify structural abnormalities, extent of damage, and potential complications. Differential diagnosis, distinguishing clubitis from other conditions with similar symptoms, ensures the most appropriate treatment plan.
Question 3: What are the common treatment approaches for clubitis?
Treatment strategies vary based on the specific case, considering the severity and underlying cause. Conservative approaches often include physical therapy, aimed at restoring mobility and managing pain. Medications, such as anti-inflammatory drugs, may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and pain. In severe cases, surgical intervention might be necessary to address significant joint damage or restore function.
Question 4: How long does recovery from clubitis typically take?
Recovery timelines vary significantly. The duration depends on factors like the severity of the condition, the chosen treatment approach, and the individual's response. Conservative management, including physical therapy and medication, may result in recovery within several weeks to months. Surgical interventions often require longer recovery periods, typically measured in months.
Question 5: What are the potential long-term implications of untreated clubitis?
Untreated clubitis can result in persistent pain, chronic inflammation, and permanent joint damage. This can lead to long-term disability, affecting the ability to perform daily tasks and impacting overall quality of life. Delayed or inadequate treatment may result in more invasive procedures later on to address the damage, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and appropriate management.
Understanding the key aspects of clubitis, as outlined above, is critical. Consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
This concludes the FAQ section. The following section will delve into the etiology of clubitis.
Conclusion
Clubitis, characterized by a range of symptoms including pain, swelling, and limited mobility, necessitates a comprehensive and individualized approach to treatment. Accurate diagnosis, crucial for effective management, relies on a thorough evaluation of symptoms, physical examination findings, and pertinent imaging studies. Conservative treatments, such as physical therapy and medication, often represent the initial therapeutic strategies. However, in severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to address significant structural damage and restore joint function. The inflammatory response is central to the condition's presentation, influencing symptom severity and necessitating targeted interventions. Understanding the interplay between symptoms, diagnosis, and various treatment options is paramount to achieving optimal patient outcomes and minimizing long-term complications. This comprehensive exploration of clubitis underscores the importance of seeking prompt medical attention for appropriate and timely intervention.
The information presented here provides a general overview of clubitis. This knowledge should serve as a foundation for further investigation and discussion with healthcare professionals. Early recognition and effective management of clubitis are essential for preserving joint function and quality of life. Continued research into the etiology and optimal treatment strategies for clubitis is vital for advancing patient care. Patients should actively engage in open communication with their healthcare providers, ensuring a shared understanding of the condition and its management, leading to positive patient outcomes.
New Movies & TV Shows On MoviesFlix Net!
New HIX Web Series: Must-Watch!
Betpawa UG - Best Online Betting In Uganda