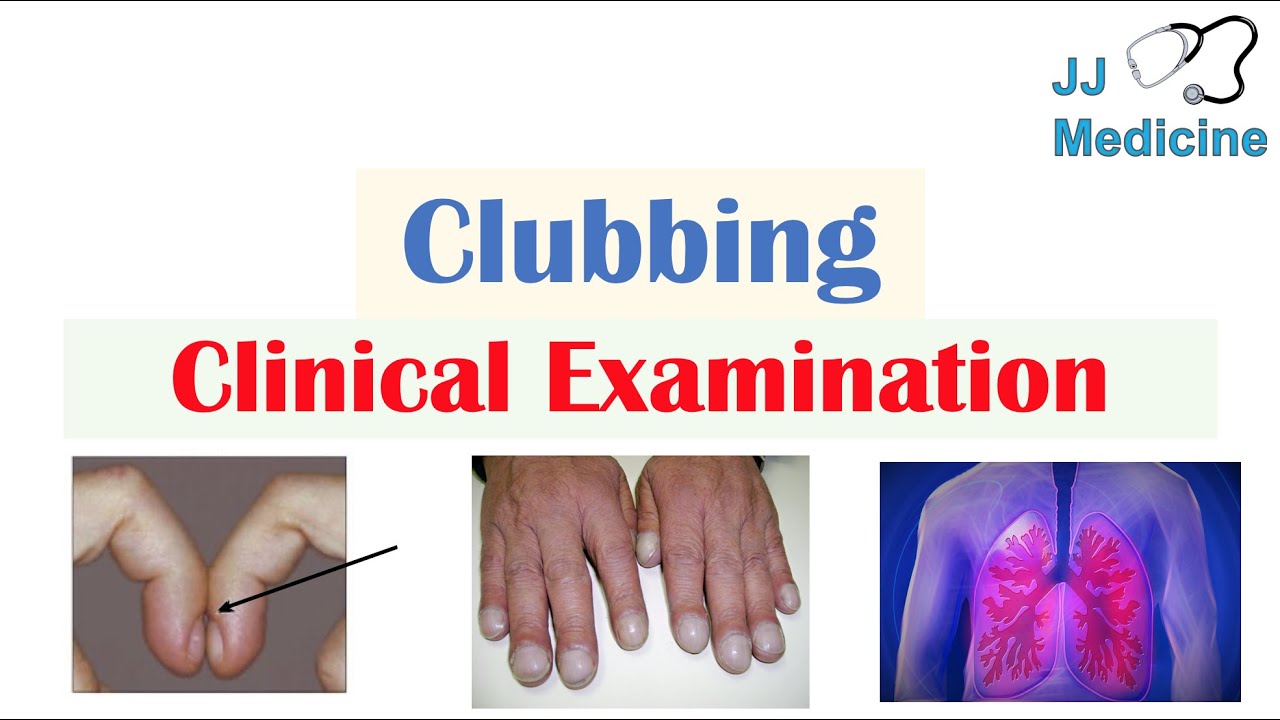
Understanding the Manifestations of this Condition: What are the Key Indicators?
The signs and indications of this condition vary, but common presentations include pain, swelling, and restricted movement in the affected joint. Specific symptoms may depend on the precise location and severity of the issue. For example, localized tenderness to the touch, accompanied by inflammation, might be indicative of the disease. Furthermore, stiffness, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity, could be a significant symptom. It's important to note that the precise nature and extent of these signs can differ among individuals and cases. Careful observation and accurate medical evaluation are crucial for appropriate diagnosis and management.
The significance of recognizing these symptoms lies in the potential for timely intervention. Early diagnosis allows for more effective treatment strategies, potentially mitigating long-term complications and improving overall outcomes. Understanding the particular symptoms allows individuals to better communicate with healthcare professionals, facilitating prompt and accurate assessment. However, it's crucial to remember that this information is for educational purposes only and should not substitute professional medical advice.
Moving forward, we will delve into specific types of affected joints, common causes, and potential treatment options.
Clubitis Disease Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of clubitis is crucial for timely intervention and effective management. Accurate identification of these indicators facilitates appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
- Joint pain
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Redness
- Limited mobility
- Tenderness
- Inflammation
These symptoms, often appearing together, indicate a possible issue within the affected joint. Pain, swelling, and stiffness, for instance, frequently manifest in conjunction with redness and tenderness. Limited mobility can significantly restrict daily activities, emphasizing the importance of prompt diagnosis and treatment. Inflammation is a key component, reflecting the body's response to the condition. These symptoms often indicate a need for medical attention and investigation into potential causes.
1. Joint Pain
Joint pain is a frequently reported symptom in conditions affecting joints, including clubitis. Understanding its various facets within the context of clubitis is vital for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
- Location and Characterization of Pain
The location of joint pain can provide clues about the underlying cause. Localized pain in a specific joint, often accompanied by tenderness to touch, may suggest a localized issue like clubitis. The character of the pain, whether sharp, dull, aching, or throbbing, can also provide valuable information. Acute, severe pain may indicate a more significant injury, while chronic, persistent pain might suggest a more insidious condition.
- Severity and Duration of Pain
The intensity of joint pain, ranging from mild discomfort to severe agony, and its duration, from fleeting to persistent, are both important factors. A gradual onset of pain, potentially over days or weeks, might indicate a developing condition like clubitis, whereas sudden, intense pain could point to a different injury or cause. The relationship between pain severity and duration is essential for differential diagnosis.
- Aggravating and Alleviating Factors
Identifying factors that exacerbate or alleviate the pain can further inform diagnosis. For instance, activities like running or weight-bearing might worsen pain associated with clubitis. Conversely, rest or application of ice could provide some relief. Understanding these patterns can help narrow down possible causes and tailor appropriate interventions.
- Associated Symptoms
Pain in a joint is rarely an isolated symptom. Presence of additional symptoms, like swelling, redness, stiffness, or restricted movement, strengthens the suspicion of clubitis or related conditions. Careful consideration of all coexisting symptoms significantly increases diagnostic accuracy.
In summary, the presence and characteristics of joint pain, along with associated symptoms, are essential elements in evaluating potential clubitis. Careful attention to the location, severity, duration, and aggravating/alleviating factors, in conjunction with associated symptoms, can help distinguish clubitis from other potential joint conditions and guide appropriate medical intervention.
2. Swelling
Swelling, a common feature in various joint conditions, plays a significant role in the clinical presentation of clubitis. Edema, or fluid accumulation within the affected joint, often accompanies pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion. The underlying mechanisms driving this swelling in clubitis are not fully elucidated but likely involve inflammatory processes, contributing to the overall clinical picture.
The presence and extent of swelling are crucial diagnostic indicators. Significant swelling, coupled with other symptoms, can strongly suggest the possibility of clubitis. Clinically, differentiating between various causes of joint swelling is essential. While swelling may signify a range of conditions, its prominence in conjunction with other symptoms, like localized pain, tenderness, and stiffness, raises the suspicion of clubitis. Observing the pattern of swelling, whether it worsens with activity or is persistent, contributes to a more complete understanding of the condition. Careful documentation and evaluation of swelling, alongside other clinical signs, are vital for accurate diagnosis and the development of appropriate management strategies.
Recognizing swelling as a component of clubitis symptoms facilitates accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. The importance of considering swelling in the context of other clinical manifestations, including the specific location of the swelling and its relationship to pain and function, allows for a comprehensive approach. Understanding the intricate connection between swelling and the other symptoms associated with clubitis is vital for the development of effective treatment plans. Further research is necessary to fully elucidate the mechanisms underlying swelling in clubitis, paving the way for more targeted and effective therapeutic interventions.
3. Stiffness
Stiffness, a frequent symptom in various joint conditions, is a critical component of clubitis disease presentations. Its presence, characteristics, and relationship to other indicators aid in diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Impact on Range of Motion
Stiffness directly limits the range of motion in affected joints. This restriction hinders normal movement and activities of daily living. For example, a patient experiencing stiffness in their elbow might find it challenging to lift objects or perform simple tasks. This limitation can significantly impair functional independence. Reduced mobility in the context of clubitis necessitates careful evaluation and management to optimize patient well-being.
- Temporal Patterns
The timing of stiffness occurrence is noteworthy. Morning stiffness, often persisting for a period of time after waking, can suggest inflammatory processes, a common aspect of many conditions, including clubitis. Conversely, stiffness that develops gradually over hours or days can signal a progressive or evolving issue. Analyzing the temporal pattern of stiffness provides crucial clues about the potential nature and progression of the condition.
- Association with Other Symptoms
Stiffness often coexists with other symptoms of clubitis. For instance, joint pain and swelling frequently accompany stiffness, indicating an inflammatory response in the affected joint. The presence of these symptom clusters heightens suspicion for clubitis and underscores the need for comprehensive assessment. Identifying patterns in symptom presentation aids diagnosis and management strategies.
- Gradual vs. Acute Stiffness
The onset of stiffness is an important criterion. Acute stiffness, appearing suddenly, might point toward a different injury or condition. Conversely, gradual stiffness over several days or weeks can indicate a progressive issue, potentially suggesting clubitis or a related inflammatory process. Distinguishing between these types of stiffness is essential for accurate assessment and appropriate interventions.
In summary, stiffness in the context of clubitis symptoms presents a significant aspect of the clinical picture. Its impact on range of motion, temporal patterns, association with other symptoms, and gradual or acute onset all contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the condition. Careful consideration of these factors is paramount for accurate diagnosis, development of effective treatment plans, and ultimately, improved patient outcomes.
4. Redness
Redness, a common symptom in various inflammatory conditions, can be a crucial component in evaluating potential clubitis. Its presence, intensity, and distribution contribute to a more complete picture of the underlying pathology. Observing redness alongside other symptoms, such as pain, swelling, and stiffness, can aid in distinguishing clubitis from other joint conditions.
- Erythema and Inflammation
Redness, or erythema, frequently accompanies inflammation. This redness is often a visible sign of increased blood flow and the presence of inflammatory mediators within the affected area. The intensity of redness can correlate with the severity of inflammation and the extent of the condition. In clubitis, redness often manifests as localized redness around the affected joint, reflecting inflammation focused on that specific region.
- Vascular Response
The body's vascular response to inflammation triggers increased blood flow to the affected area, resulting in the appearance of redness. This heightened blood flow is often accompanied by vasodilation, further contributing to the erythema. Understanding this vascular component is essential in comprehending how redness serves as an indicator of potential underlying inflammatory processes in clubitis.
- Localized vs. Generalized Redness
Localized redness, concentrated around a specific joint, strongly suggests a localized inflammatory process, potentially consistent with clubitis. Conversely, generalized redness throughout the body might indicate a more systemic condition. Differentiating between localized and generalized redness helps in identifying the nature and extent of the inflammatory response. Clinical judgment is essential in interpreting these differences within the context of other symptoms.
- Severity and Duration
The intensity and duration of redness can provide valuable information. Intense redness, lasting for an extended period, alongside other symptoms, may signify a more severe or prolonged inflammatory response. Monitoring the evolution of redness, including its response to treatment, is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of intervention strategies. Understanding these nuances is crucial for effective management of clubitis.
In conclusion, the presence of redness in clubitis is not an isolated symptom but rather a component of a broader inflammatory response. Its characteristics, including localization, intensity, and duration, can significantly aid in evaluating the extent and severity of the condition. Careful consideration of redness, alongside other clinical findings, enhances diagnostic accuracy and guides therapeutic interventions for individuals experiencing clubitis.
5. Limited Mobility
Limited mobility is a key symptom frequently observed in individuals experiencing clubitis. The restricted movement often stems from pain, swelling, and inflammation within the affected joint. This combination of factors impedes the normal range of motion, significantly impacting daily activities and overall functional capacity. For example, an individual experiencing clubitis in the knee might find it challenging to walk, climb stairs, or perform other activities requiring knee flexion or extension. Similarly, limited mobility in the elbow might hinder tasks such as lifting or grasping objects.
The clinical significance of limited mobility in clubitis extends beyond the immediate discomfort. Persistent restrictions in joint movement can lead to secondary complications, including muscle atrophy, joint contractures, and a decline in overall physical fitness. These secondary effects can create a vicious cycle, where limited mobility exacerbates the symptoms of clubitis, making it harder to engage in rehabilitation or recovery efforts. The degree of limited mobility varies among individuals, depending on the specific location and severity of clubitis. Recognizing the connection between limited mobility and clubitis is crucial for prompt intervention and preventing long-term functional limitations.
In summary, limited mobility is a crucial component of clubitis disease symptoms, directly resulting from the inflammatory processes and pain within the affected joint. Understanding this connection underscores the importance of early diagnosis and appropriate management strategies to prevent or minimize the long-term consequences of impaired mobility. Appropriate physiotherapy, coupled with other treatments, can help restore movement and function, thereby minimizing the impact of clubitis on daily life.
6. Tenderness
Tenderness, characterized by heightened sensitivity to touch in a specific area, is a crucial component of clubitis disease symptoms. The underlying cause of this tenderness often lies in inflammation within the affected joint. Inflammation triggers the release of chemical mediators, leading to increased blood flow and nerve sensitivity, thus amplifying the perception of pain and tenderness. This heightened sensitivity is a key indicator of the inflammatory process impacting the joint.
The importance of tenderness as a symptom in clubitis cannot be overstated. Its presence, combined with other clinical findings like pain, swelling, and limited range of motion, significantly strengthens the suspicion of the condition. For example, a patient experiencing localized tenderness in the ankle joint, accompanied by swelling and restricted movement, strongly suggests the possibility of clubitis. Accurate assessment of tenderness, including its location, intensity, and duration, is vital for differential diagnosis. Tenderness to palpation in the area surrounding a joint, along with other symptoms, can differentiate clubitis from other musculoskeletal conditions with similar presentations.
The practical significance of understanding tenderness in clubitis stems from its role in facilitating accurate diagnosis and guiding appropriate management strategies. Clinicians can utilize tenderness as a valuable clinical sign to support their diagnostic process. Properly assessing the characteristics of tenderness (location, intensity, and relationship to other symptoms) is instrumental in distinguishing clubitis from other conditions. Furthermore, monitoring the response of tenderness to treatment allows clinicians to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions and adjust management as necessary. Ultimately, this understanding enhances the ability to provide timely and effective care to individuals experiencing the symptoms of clubitis.
7. Inflammation
Inflammation is a fundamental component of the clinical presentation of clubitis disease symptoms. It underlies many of the observable manifestations experienced by affected individuals. Understanding the role of inflammation in this condition is crucial for both diagnosis and effective management strategies. The inflammatory response, while a protective mechanism, can also cause considerable discomfort and functional limitations.
- Cellular Response
Inflammation involves a complex cascade of cellular events. Specialized immune cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, migrate to the affected area. These cells release chemical mediators, including cytokines and chemokines, which initiate the inflammatory cascade. This cellular response results in increased blood flow and vascular permeability, leading to localized swelling and redness. This cellular recruitment and release of chemical mediators are hallmarks of acute inflammation, often observed in cases of clubitis. The extent and duration of this response contribute to the severity and duration of symptomatic manifestations.
- Vascular Changes
Inflammation is associated with alterations in blood vessel structure and function. Blood vessels dilate, allowing increased blood flow to the affected site. This increased blood flow contributes to the redness and warmth frequently observed in clubitis. Simultaneously, vascular permeability increases, permitting fluid to leak into the surrounding tissues, leading to edemathe swelling characteristic of many cases of clubitis. These vascular changes directly correlate with the clinical presentation of observable symptoms.
- Pain and Swelling
The inflammatory response is directly linked to pain and swelling, both key symptoms of clubitis. The release of chemical mediators, including prostaglandins, triggers pain receptors and contributes to the perception of discomfort. Similarly, increased vascular permeability and fluid leakage are responsible for the swelling associated with the condition. The precise mechanisms connecting inflammation to pain and swelling in clubitis require further investigation, but the correlation is clear. These symptoms are direct results of the inflammatory processes occurring in affected areas.
- Impact on Tissue Integrity
Prolonged inflammation can lead to damage or dysfunction of the affected joint tissues. Chronic inflammatory processes can contribute to cartilage degradation, potentially leading to long-term joint damage. The presence of ongoing inflammation in clubitis could potentially influence the progression of the disease, leading to more severe structural changes in the affected joint over time. A comprehensive understanding of the inflammatory process is essential to develop effective strategies for mitigating these potential long-term effects.
In conclusion, inflammation plays a pivotal role in the spectrum of symptoms associated with clubitis. Understanding the mechanisms by which inflammation influences cellular response, vascular changes, pain, swelling, and tissue integrity is fundamental for the development of targeted interventions and improved clinical management of this condition. Further research is necessary to fully comprehend the intricate relationship between inflammation and clubitis disease symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions about Clubitis Symptoms
This section addresses common inquiries regarding clubitis symptoms, aiming to provide accurate and informative answers. Understanding these aspects is crucial for recognizing and managing the condition effectively.
Question 1: What are the typical signs and symptoms of clubitis?
Answer 1: Clubitis often presents with localized pain, swelling, and stiffness in the affected joint. Additional symptoms may include redness, limited range of motion, and tenderness to the touch. The specific symptoms and their severity can vary among individuals.
Question 2: How long do clubitis symptoms typically last?
Answer 2: The duration of clubitis symptoms can vary significantly depending on the underlying cause, severity of the condition, and the effectiveness of treatment. Symptoms may resolve within a few days or persist for several weeks or months, depending on individual factors and the response to therapy.
Question 3: What causes clubitis?
Answer 3: The exact cause of clubitis is not always definitively established. Potential contributing factors include repetitive stress, trauma, infection, or underlying inflammatory conditions. Further diagnostic evaluation is crucial to pinpoint the precise etiology.
Question 4: Are there any preventative measures for clubitis?
Answer 4: Preventive measures may include avoiding repetitive strain or injury to the affected joint. Maintaining appropriate posture, practicing proper exercise techniques, and employing supportive measures like braces or splints can potentially reduce the risk of clubitis development.
Question 5: When should I seek medical attention for suspected clubitis?
Answer 5: If experiencing persistent or severe pain, swelling, or limited range of motion in a joint, immediate medical consultation is recommended. Prompt evaluation is crucial for establishing an accurate diagnosis and initiating appropriate treatment.
In summary, recognizing and understanding clubitis symptoms, their potential causes, and the importance of timely medical intervention are essential for effective management. Always consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
The subsequent section will delve into potential treatments and management strategies for clubitis.
Conclusion
This exploration of clubitis disease symptoms underscores the multifaceted nature of this condition. Key manifestations, including joint pain, swelling, stiffness, redness, limited mobility, tenderness, and inflammation, collectively highlight the significant impact on affected individuals. Accurate identification and assessment of these symptoms are crucial for prompt diagnosis and effective management strategies. The interplay between these symptoms, their varying presentations, and potential underlying causes emphasize the necessity for comprehensive clinical evaluations to distinguish clubitis from other similar conditions. The complex interplay between these symptoms necessitates a thorough understanding of each component to facilitate appropriate treatment and optimize patient outcomes.
Recognizing the potential for long-term complications and functional limitations, early intervention is paramount. Individuals experiencing persistent or severe symptoms should seek professional medical attention for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans. Further research is essential to fully elucidate the intricate mechanisms underlying clubitis, leading to more effective preventative and therapeutic interventions. The information provided here serves as a foundation for understanding, but should not substitute professional medical advice. Consult healthcare professionals for appropriate assessment and guidance.
Ultimate Miaz Girth Master Guide & Techniques
Charming Lucy Li: Romantic Moments & Inspiration
Kulhad Pizza Couple Viral Video: Watch The Original YouTube Link!